NEWS RELEASE
AT RICE:
Jeff Falk
713-348-6775
jfalk@rice.edu
Mike Williams
713-348-6728
mikewilliams@rice.edu
AT HOUSTON METHODIST:
Patti Muck
832-667-5740
pamuck@houstonmethodist.org
AT BAYLOR COLLEGE OF MEDICINE:
Kaylee Dusang
713-798-4710
kaylee.dusang@bcm.edu
Rice, Houston Methodist, Baylor College of Medicine designing noninvasive tech to aid removal of metabolic waste
HOUSTON – (Sept. 29, 2021) – How well does your sleeping brain prepare you for a new day? Researchers at Rice University backed by the U.S. Army Military Operational Medicine Research Program (MOMRP) are poised to find out.
Engineers at Rice University’s NeuroEngineering Initiative in partnership with the Institute of Biosciences and Bioengineering (IBB) and physicians at Houston Methodist Hospital and Baylor College of Medicine will develop a “sleeping cap” to analyze the cleansing flow of fluid that drains the brain of common metabolic waste during sleep.
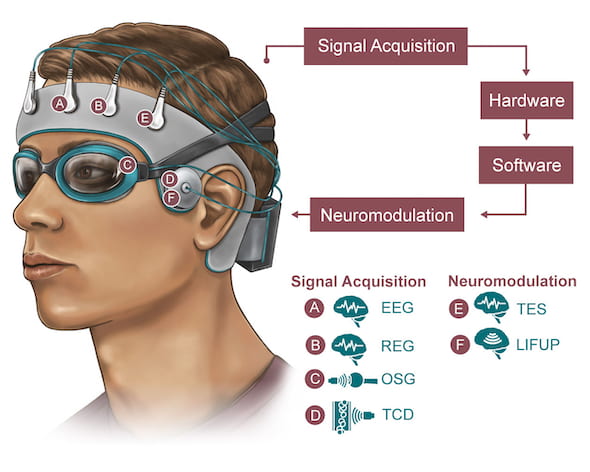
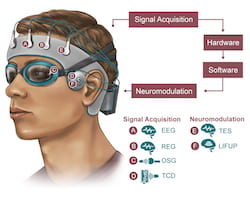
Rice University engineers, in collaboration with Houston Methodist and Baylor College of Medicine, are developing a noninvasive skullcap to better understand how the brain disposes of metabolic waste while the wearer sleeps. Signals will be acquired through electroencephalogram (EEG), rheoencephalography (REG), orbital sonography (OSG) and transcranial doppler (TCD), with modulation through transcranial/transcutaneous brain and nerve electrical simulations (TES) and low-intensity focused ultrasound pulses (LIFUP). Illustration courtesy of the NeuroEngineering Initiative
The $2.8 million award issued through the Medical Technology Enterprise Consortium is for the first year of what the research team anticipates will be a multiyear grant from the U.S. Army. The primary goal is to noninvasively measure and modulate the flow of cerebrospinal fluid as it circulates through the brain and clears waste.
Ultimately, the team aims to develop a lightweight, portable skullcap that can analyze and stimulate proper flow to treat sleep disorders in real time.

Behnaam Aazhang

Paul Cherukuri
How sleep deprivation affects soldiers is of great interest to the military, said Behnaam Aazhang, director of the NeuroEngineering Initiative and the J.S. Abercrombie Professor of Electrical and Computer Engineering at Rice.
“They want to understand the glymphatic system and what happens when soldiers lack sleep,” Aazhang said. “If a measurement says the flow is not sufficient, that’s a red flag.”
The glymphatic system pumps cerebrospinal fluid into the brain during sleep, flushing misfolded proteins and other biochemical waste, a process first described only within the past decade.
The current gold standard to view fluid flow in the brain is magnetic resonance imaging, said Paul Cherukuri, executive director of the IBB.
“Since an MRI can’t be easily transported, the Department of Defense asked if we can design a small, portable cap that can measure and modulate the brain health of warfighters during sleep to enhance their performance,” he said. “Developing this prototype will require us to start with off-the-shelf devices and learn from them in parallel with building our own sensor technology and algorithms at Rice.
“What makes this exciting is that nobody’s ever attempted to build anything quite like this before,” Cherukuri said.

Gavin Britz

Eugene Golanov
“We’re aiming for something practical and portable that is easy to use and can be available to soldiers and patients all the time,” Aazhang added.
Dr. Eugene Golanov and Dr. Gavin Britz of Houston Methodist became interested in the field after discovering disturbances in the glymphatic system after a brain hemorrhage.
“We demonstrated that abnormalities of this system affect the brain,” said Britz, the Candy and Tom Knudson Centennial Chair in Neurosurgery and director of the Houston Methodist Neurological Institute, who will lead the clinical effort. “Sleep is the body’s natural method of clearing these abnormalities.”
Houston Methodist approached Rice engineers to collaborate and develop a device to better understand and one day manipulate the glymphatic system.
“This unprecedented collaboration will not only give us more ideas for helping our soldiers in the field but also provide the spark for investigating and treating all brain diseases quickly and in real time,” Britz said. “This will crack open a new field of gathering brain data noninvasively, and it’s never been done before.”
Rice engineers will develop the technology to be evaluated at Houston Methodist and Baylor through work with healthy volunteers and patients. They expect to use several techniques, including ultrasound stimulation and electromagnetic signaling, to measure interstitial fluid as it flows out of the brain to the lymphatic system for disposal.

Ashok Veeraraghavan

Taiyun Chi
Aazhang and Cherukuri, along with Rice electrical and computer engineers Taiyun Chi, an assistant professor, and Ashok Veeraraghavan, a professor, will collaborate on the hardware and software development.
Golanov, a professor of research and co-director with Britz of the hospital’s Cerebrovascular Research Lab, and senior scientist Angelique Regnier-Golanov will be part of the effort at Houston Methodist. At Baylor, Dr. Fidaa Shaib, an associate professor of medicine in the section of pulmonary, critical care and sleep medicine, will oversee sleep assessment, evaluation and monitoring.
The final device will ideally combine and analyze multiple streams of data through machine-learning software to be developed at Rice. The merged data will eventually allow clinicians to get a real-time picture of how well the brain is clearing itself.
To start, Houston Methodist and Baylor clinicians will gather data from participants through sleep questionnaires, activity and sleep-tracking devices and commercially available headsets that monitor cerebrospinal fluid flow and compare them with MRI results.

Fidaa Shaib

Angelique Regnier-Golanov
“While humans spend almost one-third of their lives sleeping, a unifying theory about the role of sleep and its impact on human survival and function has not been identified yet,” Shaib said. “Technologies that facilitate clearing wastes and preventing their deposition in the brain are relevant to patients with sleep disorders, especially those at risk for such neurodegenerative diseases as Alzheimer’s.”
The researchers expect to deliver preliminary results of their work in a year.
-30-
Follow Rice News and Media Relations via Twitter @RiceUNews.
Related materials:
Rice Neuroengineering Initiative: https://neuroengineering.rice.edu
George R. Brown School of Engineering: https://engineering.rice.edu
Institute of Biosciences and Bioengineering: https://ibb.rice.edu
Images for download:
https://news2.rice.edu/files/2021/09/1004_BRAIN-1-web.jpg
Rice University engineers, in collaboration with Houston Methodist and Baylor College of Medicine, are developing a noninvasive skullcap to better understand how the brain disposes of metabolic waste while the wearer sleeps. Signals will be acquired will be through electroencephalogram (EEG), rheoencephalography (REG), orbital sonography (OSG) and transcranial doppler (TCD), with modulation through transcranial/transcutaneous brain and nerve electrical simulations (TES) and low-intensity focused ultrasound pulses (LIFUP). (Credit: NeuroEngineering Initiative/Rice University)
Located on a 300-acre forested campus in Houston, Rice University is consistently ranked among the nation’s top 20 universities by U.S. News & World Report. Rice has highly respected schools of Architecture, Business, Continuing Studies, Engineering, Humanities, Music, Natural Sciences and Social Sciences and is home to the Baker Institute for Public Policy. With 4,052 undergraduates and 3,484 graduate students, Rice’s undergraduate student-to-faculty ratio is just under 6-to-1. Its residential college system builds close-knit communities and lifelong friendships, just one reason why Rice is ranked No. 1 for lots of race/class interaction and No. 1 for quality of life by the Princeton Review. Rice is also rated as a best value among private universities by Kiplinger’s Personal Finance.